The ketogenic diet, often called the “keto diet,” has taken the health and wellness world by storm in recent years. But what is the keto diet, and why is it so popular? Rooted in science and widely adopted for its potential benefits such as weight loss and improved energy levels, the keto diet focuses on a high-fat, low-carbohydrate eating pattern that shifts your body into a ketosis metabolic state. Let’s tell you everything you need to know about this dietary approach, its benefits, challenges, and how to get started.

- What Is the Keto Diet?
- Why Follow the Keto Diet? Key Health Benefits
- Getting Started with the Keto Diet
- Challenges of the Keto Diet
- Is the Keto Diet Right for You?
- Real-Life Success Stories
- Tips for Long-Term Success
- FAQs About What is the keto diet
- 1. What is the keto diet?
- 2. How does the keto diet work?
- 3. What foods can I eat on the keto diet?
- 4. What are the benefits of the keto diet?
- 5. What is ketosis?
- 6. Can the keto diet help me lose weight?
- 7. What are the everyday challenges of the keto diet?
- 8. What is the keto flu, and how can I manage it?
- 9. Is the keto diet safe for everyone?
- 10. How long does it take to reach ketosis?
- 11. Do I need to track my macros on keto?
- 12. Can I eat fruit on the keto diet?
- 13. What are some easy keto meal ideas?
- 14. Will I feel tired when starting the keto diet?
- 15. Can the keto diet improve my blood sugar levels?
- 16. Are there different types of keto diets?
- 17. How do I know if I’m in ketosis?
- 18. Can I eat out while on the keto diet?
- 19. What supplements should I consider on the keto diet?
- 20. How can I make the keto diet sustainable long-term?
- Final Thoughts
- S, please consult a health professional.
What Is the Keto Diet?
The keto diet is a low-carbohydrate, moderate-protein, high-fat diet designed to send your body into ketosis, a natural metabolic process. Typically, the human body relies on carbohydrates as its primary energy source. However, when you significantly reduce carb intake, your body begins using fat for fuel instead, converting it into molecules called ketones that supply energy for your brain, muscles, and other organs.
The keto diet originated nearly a century ago as a therapeutic tool for managing epilepsy, particularly in children. Today, it is widely used not only for specific medical conditions but also to support weight loss, improve metabolic health, and even boost mental clarity.
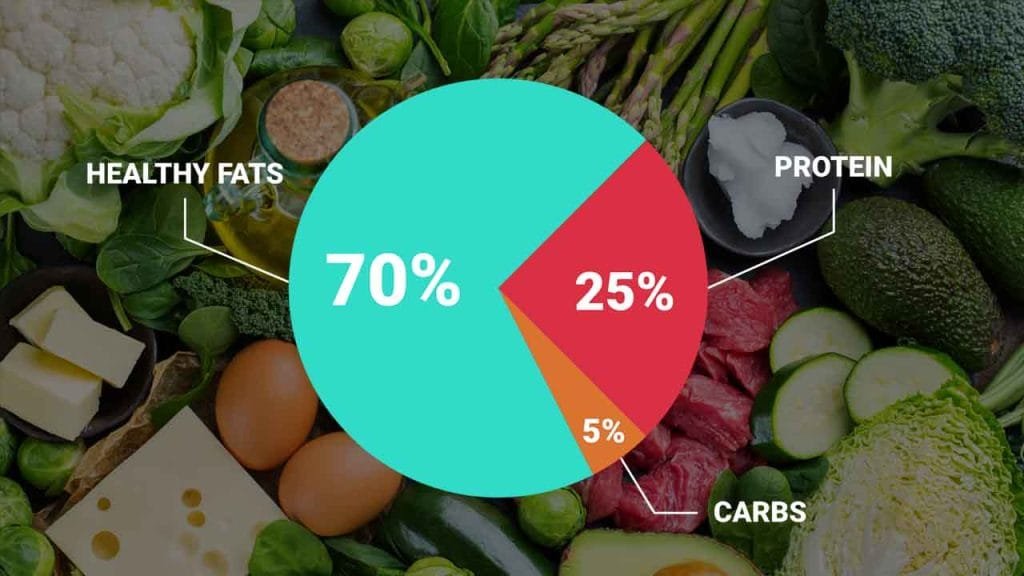
Macronutrient Breakdown of Keto
A standard ketogenic diet generally contains:
- 75% fats (from sources like oils, nuts, seeds, and avocados)
- 20% protein (found in meat, poultry, fish, or plant-based alternatives)
- 5% carbohydrates (mainly from low-carb vegetables)
This breakdown minimizes glucose production and encourages the production of ketones, leading to the fat-burning benefits the diet is known for.
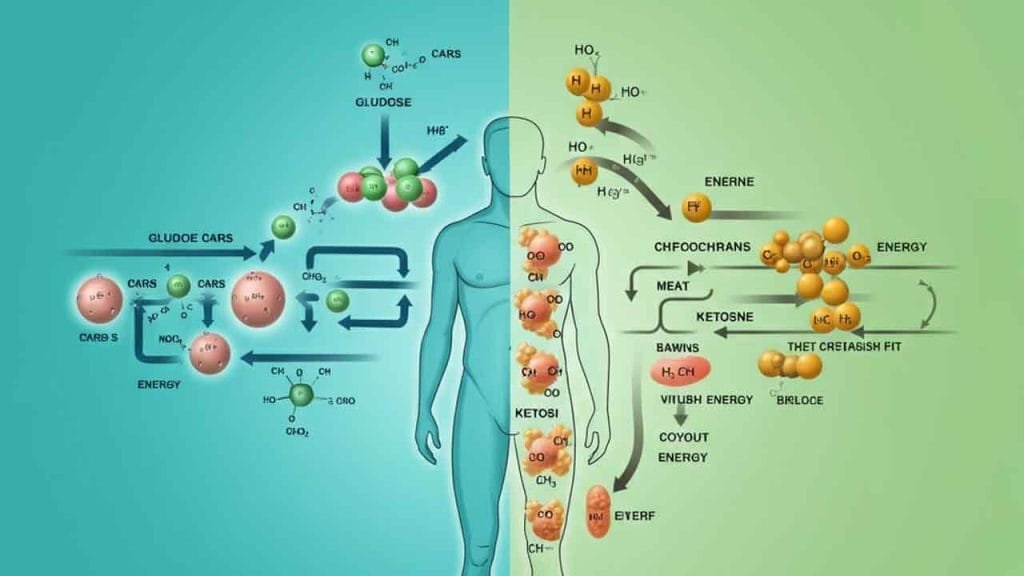
How Does Ketosis Work?
Ketosis occurs when carb intake is reduced to approximately 20-50 grams daily, depending on factors like activity level and metabolism. Without enough carbohydrates to break down into glucose, the liver starts converting fat stores into ketones, which are used for energy. This shift helps the body burn fat more efficiently and improves its metabolic processes.

Why Follow the Keto Diet? Key Health Benefits
People adopt the keto diet for various reasons, ranging from weight loss to better mental focus. Here are some of the most commonly discussed benefits:
1. Weight Loss
One of the primary reasons people turn to the keto diet is its potential for rapid weight loss. Your body converts stored fat into fuel by drastically reducing carbs and prioritizing fat and protein. Research shows that low-carb diets like keto can lead to more significant weight loss in the short term compared to traditional calorie-restricted diets.
2. Improved Blood Sugar and Insulin Levels
For individuals with type 2 diabetes or insulin resistance, the keto diet may help stabilize blood sugar and improve insulin sensitivity. A low carbohydrate intake reduces glucose fluctuations and keeps insulin levels more stable.
3. Enhanced Mental Clarity and Focus
Ketones are considered an efficient fuel source for the brain. Many people report improved mental clarity and sustained focus, likely due to the stabilization of blood sugar levels and the brain’s reliance on ketones for energy.
4. Better Energbrains
Without the energy crashes that often follow a high-carb meal, keto followers typically feel more energized throughout the day. Eating primarily fats and proteins provides a steady source of fuel.
5. Support for Certain Medical Conditions
Beyond weight loss, the keto diet has been explored as a potential dietary intervention for various medical conditions, including:
- Epilepsy (its original intended use)
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
- Alzheimer’s disease
- Certain cancers (as part of a complete treatment plan)
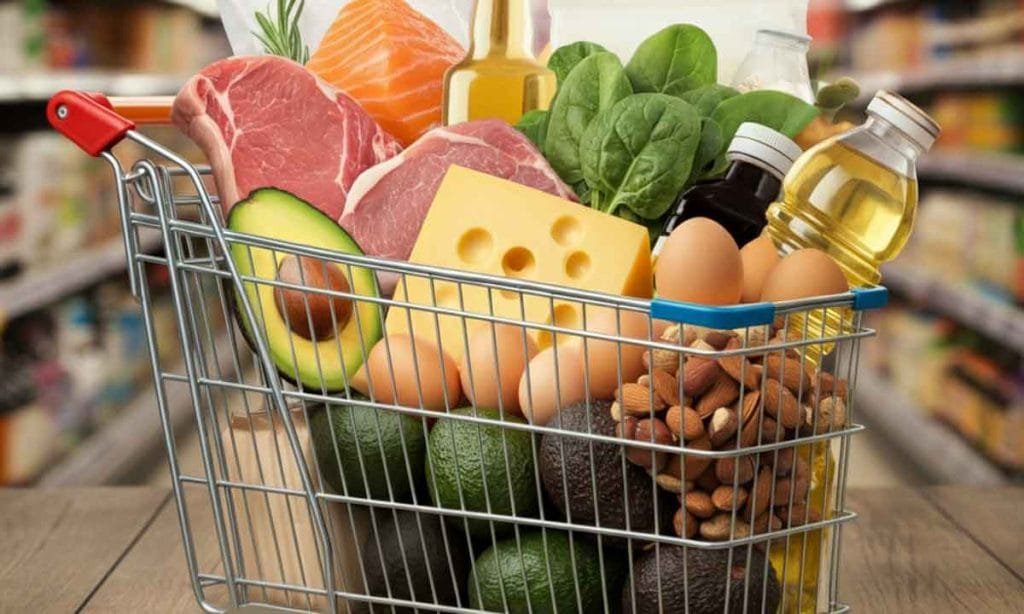

Getting Started with the Keto Diet
Transitioning to the keto lifestyle might seem overwhelming at first, but with careful planning, it doesn’t have to be. Here’s how to begin:
1. Calculate Y doesn’tros‘s
Starting the keto diet is understanding how much fat, protein, and carbs you should eat daily. Online tools like keto calculators can help you determine your macronutrient needs based on age, weight, activity level, and goals.
2. Stock Up on Keto-Friendly Foods
Some of the most popular foods on the keto diet include:
- Healthy Fats: Avocados, olive oil, butter, coconut oil, and nuts
- Protein Sources: Beef, chicken, fish, eggs, and tofu
- Low-Carb Vegetables: Spinach, broccoli, zucchini, kale, and cauliflower
- Other Staples: Cheese, unsweetened almond milk, and keto-friendly sweeteners like stevia
Avoid high-carb foods like bread, pasta, rice, pastries, and sugary snacks.
3. Meal Planning
Planning meals can make sticking to your carb and fat targets easier. Consider preparing breakfast, lunch, and dinner recipes that fit the keto guidelines. For example:
- Breakfast: Scrambled eggs with avocado and bacon
- Lunch: Grilled chicken salad with olive oil dressing
- Dinner: Baked salmon with cauliflower rice
4. Stay Hydrated
Low-carb diets can lead to fluid loss, so drink plenty of water. Adding electrolyte-rich foods or supplements can help prevent dehydration.
5. Monitor Your Progress
Track your macronutrients daily with an app or food diary. Many keto followers also measure ketone levels using urine strips or a blood monitor to ensure they’ve entered ketosis.
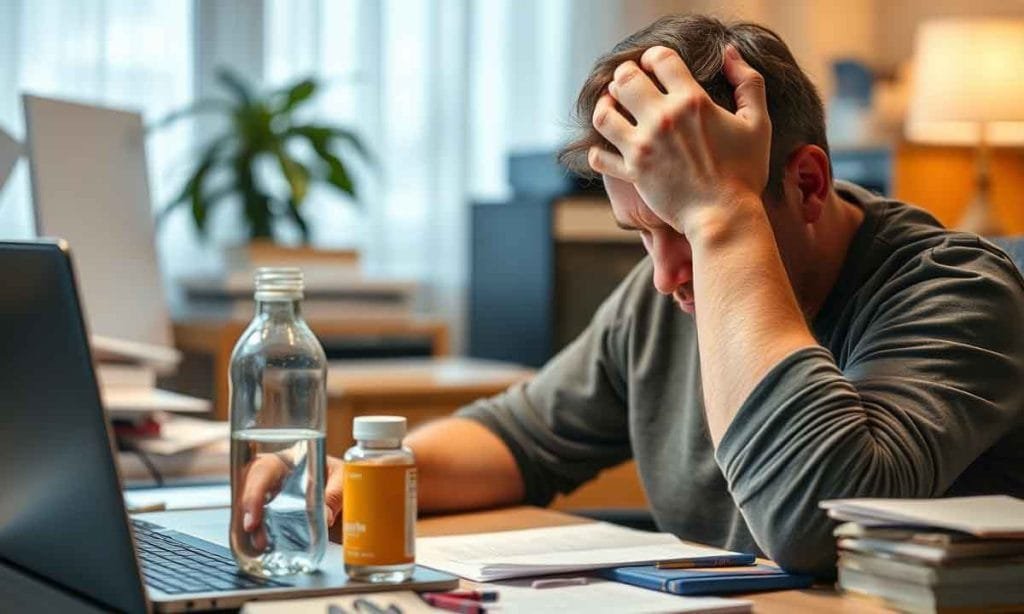

Challenges of the Keto Diet
Although the keto diet offers many benefits, it’s not without challenges. Here are some common issues people face:
1. The Keto Flu
When starting the diet, individuals report flu-like symptoms such as fatigue, headaches, and irritability. This occurs as the body adapts to burning fat instead of carbs. Increasing fluid intake and electrolytes can help alleviate these symptoms.
2. Restrictive Nature
Adhering to such a strict eating plan can feel restrictive, especially in social settings where high-carb foods dominate. Some people find it hard to maintain this diet long-term.
3. Nutrient Deficiencies
Eliminating fruits, grains, and legumes can lead to specific vitamin and mineral deficiencies. You may need to take supplements to meet your nutritional needs.
4. Digestive Changes
The sudden increase in fat and reduced fiber-rich foods may cause digestive issues like constipation. To counter this, include keto-friendly, fiber-rich vegetables in your meals.

Is the Keto Diet Right for You?
The keto diet isn’t a one-size-fits-all approach and may not be suitable for everyone. People with certain medical conditions, such as kidney disease, should avoid it. In contrast, others should consult their doctor before starting, particularly if they’re pregnant, breastfeeding, or on medication for diabetes or high blood pressure.
They might be worth trying for health goals like weight loss or improved energy levels. However, as with any diet, success depends on consistency, planning, and how well it fits your lifestyle.
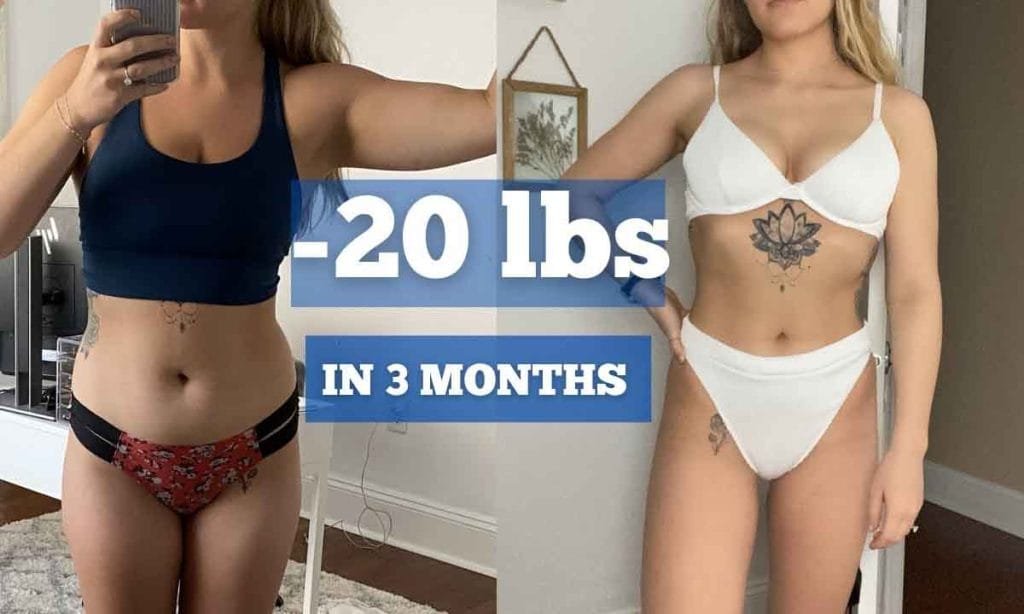
Real-Life Success Stories
Many individuals have shared inspiring stories of how the keto diet changed their health. For example, Sarah, a 35-year-old mother of two, lost 20 pounds in three months and reported enhanced focus and energy. Similarly, Jake, a 42-year-old with type 2 diabetes, noticed significant improvements in his blood sugar levels after just six weeks.
Personal testimonies like these highlight the potential impact of following a ketogenic lifestyle.
Tips for Long-Term Success
To maintain long-term success on the keto diet:
- Focus on Whole, Unprocessed Foods: Avoid “keto junk food” and choose real food options.
- Customize Your Plan: Adjust your macronutrient goals based on your progress and preferences.
- Stay Educated: Learn keto-friendly recipes and tips to continue enjoying the lifestyle.
- Be Flexible: Allow occasional off-plan meals without guilt to sustain your diet long-term.
FAQs About What is the keto diet
1. What is the keto diet?
The keto diet is a low-carbohydrate, high-fat diet that encourages your body to enter a metabolic state called ketosis. In this state, your body burns fat for energy instead of carbohydrates, which can lead to weight loss and other health benefits.
2. How does the keto diet work?
The keto diet works by drastically reducing your intake of carbs (to about 20-50 grams per day) while increasing fats. This forces your body to produce ketones from fat, which are then used as an alternative energy source.
3. What foods can I eat on the keto diet?
Keto-friendly foods include healthy fats (avocados, olive oil, nuts), proteins (meat, fish, eggs), and low-carb vegetables (spinach, cauliflower, zucchini). Avoid high-carb foods like bread, pasta, rice, sugary snacks, and starchy vegetables.
4. What are the benefits of the keto diet?
The keto diet may support weight loss, improve blood sugar and insulin levels, boost mental clarity, and enhance energy levels. It’s also used as a dietary intervention for conditions like epilepsy and polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS).
5. What is ketosis?
Ketosis is a natural process in which the body burns fat for fuel instead of glucose. It occurs when carbohydrate intake is very low, and the body produces ketones for energy.
6. Can the keto diet help me lose weight?
Yes, many people experience weight loss on the keto diet because it encourages the body to burn stored fat for energy. Studies suggest it can be more effective for short-term weight loss than traditional low-fat diets.
7. What are the everyday challenges of the keto diet?
Challenges include the “keto flu” (symptoms like fatigue and headaches when transitioning), restricted food choices, potential nutrient deficiencies, and digestive changes like constipation.
8. What is the keto flu, and how can I manage it?
The keto flu refers to flu-like symptoms that occur during the first few days of starting keto. Symptoms include headaches, fatigue, and irritability. Staying hydrated and replenishing electrolytes can help alleviate these symptoms.
9. Is the keto diet safe for everyone?
The keto diet may not be suitable for individuals with certain conditions, like kidney disease, or those who are pregnant or breastfeeding. Always consult with a healthcare professional before starting.
10. How long does it take to reach ketosis?
It typically takes 2-4 days of following a strict low-carb diet to enter ketosis, although it can vary depending on factors like metabolism and activity level.
11. Do I need to track my macros on keto?
Yes, tracking your macronutrient intake (fats, proteins, and carbs) is essential to ensure you stay within keto guidelines and achieve ketosis.
12. Can I eat fruit on the keto diet?
Most fruits are high in sugar and carbs, but small amounts of low-carb fruits like berries can be included in moderation.
13. What are some easy keto meal ideas?
Examples include scrambled eggs with avocado and bacon for breakfast, grilled chicken salad with olive oil for lunch, and baked salmon with cauliflower rice for dinner.
14. Will I feel tired when starting the keto diet?
You might feel tired initially as your body adjusts to burning fat instead of carbs, but energy levels typically improve once you’re fully in ketosis.
15. Can the keto diet improve my blood sugar levels?
Yes, the keto diet can stabilize blood sugar by reducing glucose intake, making it a potential option for people with type 2 diabetes or insulin resistance.
16. Are there different types of keto diets?
Yes, popular variations include the standard ketogenic diet (SKD), cyclical ketogenic diet (CKD), and targeted ketogenic diet (TKD). Each is tailored to different goals, such as athletic performance or weight loss.
17. How do I know if I’m in ketosis?
You can test ketone levels using urine strips, a breath analyzer, or a blood meter. Common signs of ketosis include increased energy, reduced appetite, and a metallic taste in the mouth.
18. Can I eat out while on the keto diet?
Yes, many restaurants offer keto-friendly options. Opt for protein-rich meals with non-starchy vegetables, and ask for sauces or dressings on the side to control hidden carbs.
19. What supplements should I consider on the keto diet?
Supplements like magnesium, potassium, and sodium can help replenish electrolytes. You might also consider omega-3 fatty acids or fiber supplements to support overall health.
20. How can I make the keto diet sustainable long-term?
To stay on track for the long term, focus on whole, unprocessed foods, plan meals, and allow occasional flexibility to enjoy social events or treat meals without guilt.
Final Thoughts
The ketogenic diet is much more than a passing trend. Whether aiming for weight loss, improved energy, or better metabolic health, it offers a research-backed approach to achieving your goals. However, it’s essential to understand the changes this lifestyle and prepare for the challenges along the way.
If you’re ready to take control of your health and try the keto diet, start small, stay consistent, and remember that everyone’s experience will differ before beginning any significant dietary change that aligns with your health needs.
S, please consult a health professional.
Dive into the keto lifestyle today and discover whether it’s the right approach for supporting your unique health goals!


