The ketogenic (keto) diet has become popular for weight loss, improved energy levels, and better mental clarity. But if you’re new, you may wonder, how many grams of carbs per day on keto should you consume? The answer is pivotal in achieving and maintaining ketosis, the metabolic state where your body burns fat for fuel instead of carbs.
This comprehensive guide will demystify carb intake on keto, teach you how to count carbs correctly, and help you succeed in your keto journey while prioritizing your health.

- What Is a Keto Diet?
- How Many Grams of Carbs Per Day on Keto?
- Why 20-50 Grams of Carbs?
- How to Calculate Your Keto Carb Limit
- Types of Carbs to Include on Keto
- Exceptional Cases: Adjusting Carbs for Different Goals
- Real-Life Examples of Keto Meals
- Common Mistakes to Avoid
- How to Measure Progress
- FAQs About How Many Grams of Carbs Per Day on Keto?
- 1. What is the recommended daily carb intake on the keto diet?
- 2. What are net carbs, and how do I calculate them?
- 3. Why is keeping carb intake low important on keto?
- 4. Can I eat more than 50 grams of carbs and still be in ketosis?
- 5. What foods should I avoid on keto?
- 6. What are some good low-carb food options on keto?
- 7. Is the keto diet suitable for everyone?
- 8. How can I tell if I’m in ketosis?
- 9. What happens if I go over my daily carb limit?
- 10. Can I work out while on keto?
- 11. What is the “keto flu,” and how can I avoid it?
- 12. Do I need to count calories on keto?
- 13. Can I follow keto if I’m vegetarian or vegan?
- 14. How long should I stay on the keto diet?
- 15. Can I drink alcohol on keto?
- 16. How do I maintain my weight after keto?
- 17. Is keto only for weight loss?
- Wrapping Up: Is Keto Right for You?
What Is a Keto Diet?
The ketogenic diet focuses on drastically reducing carbohydrate intake while increasing fat consumption and maintaining moderate protein intake. By doing so, your body transitions from using carbs as its primary fuel source to burning fat. This process produces ketones, molecules that supply energy when glucose is scarce.
This metabolic shift is termed ketosis, and it’s behind the keto diet, which has gained recognition for its numerous benefits, including weight loss, appetite control, and even potential improvements in conditions like Type 2 diabetes and epilepsy.
But understanding your carb intake is the foundation of maintaining ketosis.
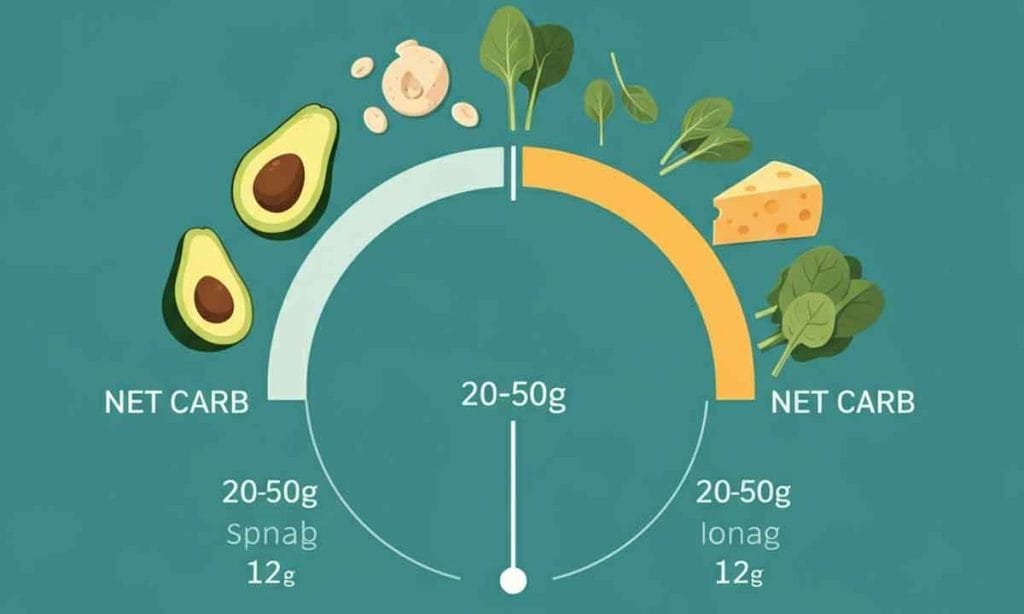

How Many Grams of Carbs Per Day on Keto?
The standard ketogenic diet recommends 20-50 grams of net carbs daily. This range ensures that you limit the glucose available to your body, pushing it to switch to ketones for energy.
Your ideal carb intake depends on age, activity level, body composition, and health goals. Some individuals may achieve ketosis with slightly higher carb limits, while others need stricter constraints.
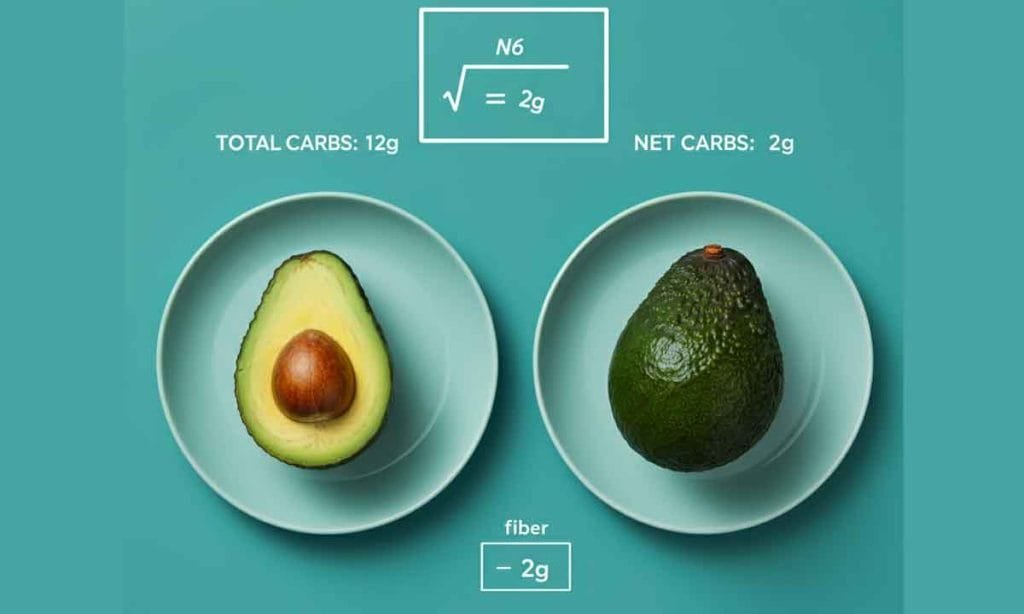
What Are Net Carbs?
Understanding the concept of “n” t carbs” “s “essenti” l “for tracking carbs effectively. Net carbs represent the total carbohydrates in a food minus the fiber and sugar alcohols. Since fiber and certain sugar alcohols don’t affect blood sugar levels, they don’t count towards your daily carb allowance.
For example:
- Total carbs in an avocado (1 cup): 12g
- Fiber content: 10g
- Net carbs = 12g – 10g = 2g
When calculating net carbs, always check food labels or use a trusted tracking app to ensure accuracy.

Why 20-50 Grams of Carbs?
The magic range of 20-50 grams daily is grounded in science. For most people, sticking to this limit ensures that insulin levels remain low and glycogen stores stay depleted, conditions ideal for ketosis. Here’sangeookss like:
- 20 grams of net carbs/day (strict): Suitable for those with insulin resistance, severe metabolic conditions, or individuals aiming for rapid weight loss.
- 30-50 grams of net carbs/day (moderate): This range allows for slightly more flexibility while enabling ketosis for most people. It may better suit active individuals or those who prefer a less restrictive plan.
If you’re not getting the results you want, it could mean your carb intake is too high, preventing you from entering ketosis. Testing your ketone levels with urine strips or a blood monitor can provide insight into whether adjustments are needed.

How to Calculate Your Keto Carb Limit
While 20-50 grams is a general guideline, using your macronutrient needs will give you the most personalized and effective keto plan. Here’s how to calculate:
- Determine Your Total Caloric Needs. Use an online calculator to determine how many calories you need to maintain or lose weight.
- Set a Macronutrient Ratio. The standard keto macronutrient breakdown is:
- 5-10% carbs
- 20-25% protein
- 70-80% fat
- Convert Percentage to Grams. For carbs, multiply your total caloric needs by 5% (or 0.05), then divide by 4 (since each gram of carbs contains four calories).
Example for a 2,000-calorie diet:- 2,000 x 0.05 = 100 calories from carbs
- 100 ÷ 4 = 25 grams of carbs/day
This approach ensures the percentage of carbs you consume aligns with your energy needs and goals.

Types of Carbs to Include on Keto
Not all carbs are created equal. The quality of carbs you choose can impact your health and your adherence to the keto diet.
Best Low-Carb Foods for Keto:
- Non-starchy vegetables: Leafy greens, broccoli, cauliflower, zucchini
- Berries: Blueberries, raspberries, blackberries (in moderation)
- Nuts and seeds: Almonds, walnuts, chia seeds
- Healthy fats: Avocado, olives
- Low-carb dairy: Cheese, full-fat Greek yogurt, heavy cream
These foods are packed with nutrients and fiber, helping you stay full and nourished while keeping carb intake low.

Foods to Strictly Avoid:
- Sugary foods (soda, cakes, candies)
- Refined grains (white bread, rice, pasta)
- Starchy vegetables (potatoes, corn, peas)
- High-carb fruits (bananas, apples, mangos)
By prioritizing nutrient-dense foods, you’ll maintain your health while supporting your overall health.

Exceptional Cases: Adjusting Carbs for Different Goals
The standard carb guidelines may need adjustment based on your specific needs or circumstances:
1. Active Individuals:
You’ll allow a targeted diet to die if you diet, especially with high-intensity workouts, a high-intensity approach will enable you to strategically time 20-50 grams of fast-digesting carbs before or after exercise to replenish glycogen without disrupting ketosis.
2. Therapeutic Keto (Medical Conditions):
For therapeutic purposes, such as managing epilepsy or neurological disorders, stricter carb limits (often under 20 grams/day) are typically advised.
3. Keto for Weight Maintenance:
If you’ve achieved your goal and want to maintain your weight while burning fat as fuel, you may expand to a more liberal low-carb diet, consuming up to 100 grams/day. However, this often moves you out of ketosis.
Monitoring your progress and tweaking your carb intake to meet your lifestyle and goals is key to sustained success.
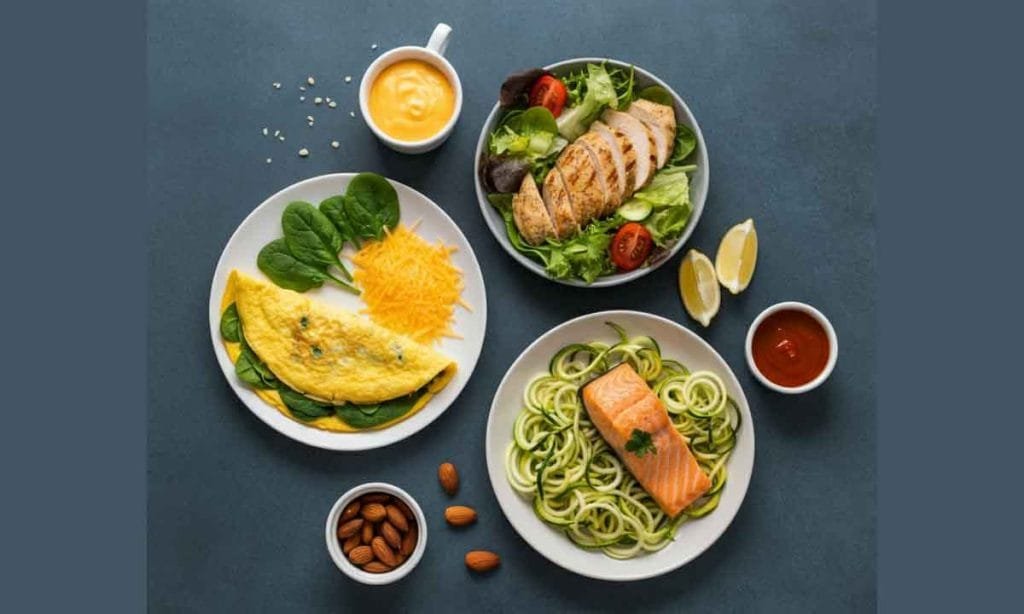

Real-Life Examples of Keto Meals
Here are a few sample meals and their approximate net carb content:
Breakfast:
- Keto Omelette: 2 eggs, spinach, mushrooms, cheese
- Net carbs: 4g
Lunch:
- Grilled Chicken Salad: Romaine lettuce, olive oil dressing, avocado slices
- Net carbs: 6g
Dinner:
- Zucchini Noodles with Pesto and Salmon:
- Net carbs: 8g
Snack:
- Handful of almonds (1oz):
- Net carbs: 2g
These meals are rich in fats, moderate in protein, and low in carbohydrates, which helps you stay in ketosis.

Common Mistakes to Avoid
Starting keto can feel overwhelming, so steer clear of these common pitfalls:
- Not Reading Labels: Many packaged foods label carbs deceptively. Always check the total and net carbs.
- Ignoring Hidden Carbs: Sauces, condiments, or keto-friendly snacks, contain hidden sugars.
- Overeating Protein: Excess protein can convert into glucose through gluconeogenesis, potentially kicking you out of ketosis.
- Neglecting Micronutrients: Focus on electrolytes like sodium, potassium, and magnesium to avoid keto flu symptoms.
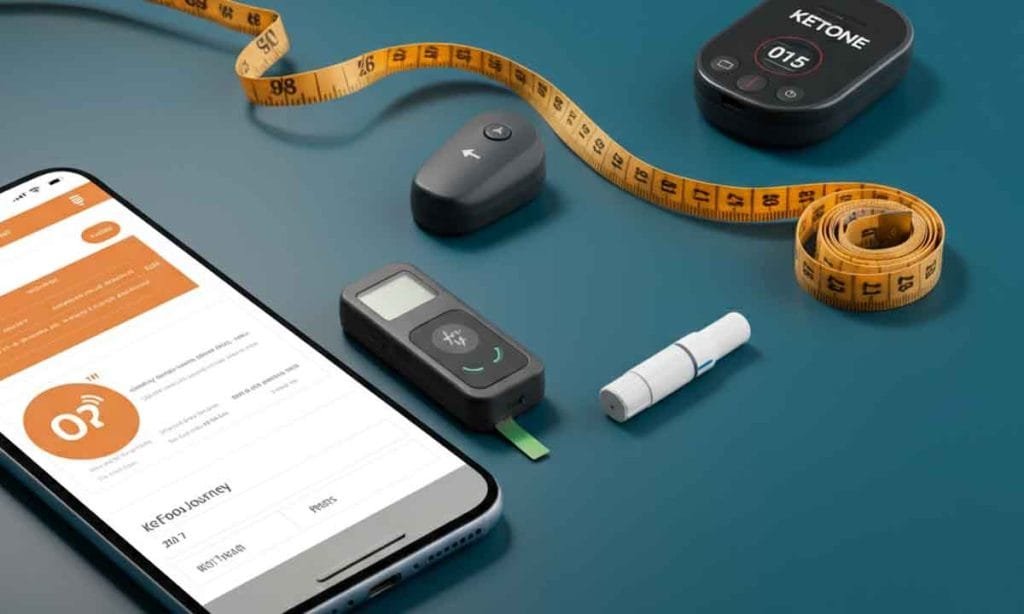

How to Measure Progress
Tracking your progress is key to understanding if your carb intake is proper. Here are tools and techniques:
- Ketone Testing: Use urine strips or a blood monitor to measure ketones.
- Food Diary Apps: Apps like MyFitnessPal allow you to log meals and calculate net carbs accurately.
- Body Measurements: Beyond weight, track changes in body fat percentage, clothing fit, and energy levels.
FAQs About How Many Grams of Carbs Per Day on Keto?
1. What is the recommended daily carb intake on the keto diet?
The standard ketogenic diet recommends 20-50 grams of net carbs daily. This range helps most people enter and maintain ketosis, allowing the body to burn fat for fuel instead of carbs.
2. What are net carbs, and how do I calculate them?
Net carbs are the total carbohydrates in a food minus the fiber and certain sugar alcohols, as these don’t raise blood sugar levels. For instance, a food with 15g of total carbs and 10g of fiber has 5g net carbs.
3. Why is keeping carb intake low important on keto?
Minimizing carbs keeps insulin levels low and depletes glycogen stores, prompting the body to use fat as its primary energy source. This state, called ketosis, is key to reaping the diet’s benefits, such as weight loss and improved energy.
4. Can I eat more than 50 grams of carbs and still be in ketosis?
It depends on your body. Some individuals, especially those highly active, may tolerate slightly more carbs and remain in ketosis. However, for most people, staying under 50 grams is safest to maintain ketosis.
5. What foods should I avoid on keto?
Avoid high-carb foods like:
Sugary snacks (candy, soda, desserts)
Refined grains (white bread, pasta, rice)
Starchy veggies (potatoes, corn, carrots)
High-carb fruits (bananas, apples, mangos)
Stick to low-carb, nutrient-dense options to stay in ketosis.
6. What are some good low-carb food options on keto?
Focus on these:
Non-starchy vegetables (spinach, zucchini, broccoli)
Healthy fats (avocado, olive oil)
Nuts and seeds (almonds, chia seeds)
Low-carb dairy (cheese, heavy cream)
Small portions of berries (blueberries, raspberries)
These foods will help maintain ketosis and provide essential nutrients.
7. Is the keto diet suitable for everyone?
The keto diet may not be ideal for everyone, especially those with certain medical conditions like kidney issues, liver problems, or a history of eating disorders. Pregnant or breastfeeding women and those under certain medications should consult a healthcare professional before starting.
8. How can I tell if I’m in ketosis?
You can test your ketosis levels using:
Urine test strips: Easy and inexpensive but less accurate.
Blood ketone monitors: Provide precise measurements.
Signs of ketosis may include reduced appetite, increased energy, and a distinct “keto breath.”
9. What happens if I go over my daily carb limit?
Exceeding your carb limit can kick you out of ketosis, causing your body to switch back to using glucose for energy. If this happens, return to your carb limit the next day to re-enter ketosis.
10. Can I work out while on keto?
Yes, you can! While your body adjusts (during the first 1-2 weeks), you might feel a dip in performance. After adaptation, many people report improved endurance and steady energy. Active individuals may benefit from the targeted keto diet, which allows small pre- or post-workout carb intakes.
11. What is the “keto flu,” and how can I avoid it?
“Keto flu” refers to temporary symptoms like fatigue, headaches, and irritability during your body’s transition into ketosis. You can minimize this by:
Staying hydrated
Replenishing electrolytes (sodium, potassium, magnesium)
Eating enough healthy fats for energy
12. Do I need to count calories on keto?
Not necessarily! Many people naturally eat fewer calories on keto because high-fat foods are satiating. However, if you’re not reaching your goals, tracking calories alongside carbs might help.
13. Can I follow keto if I’m vegetarian or vegan?
Yes! A plant-based keto diet focuses on low-carb foods like non-starchy vegetables, nuts, seeds, tofu, and plant-based oils (coconut, avocado). It may require more planning to meet protein and fat needs, but it’s possible.
14. How long should I stay on the keto diet?
The duration depends on your goals. Some people adopt keto as a long-term lifestyle, while others use it for short-term weight loss or specific health benefits. Discuss this with a healthcare professional to determine what’s best for you.
15. Can I drink alcohol on keto?
Alcohol can be consumed in moderation, but choose low-carb options like dry wines or spirits (vodka, whiskey) mixed with soda water. Be mindful of your overall carb intake.
16. How do I maintain my weight after keto?
If you reach your goal, transitioning to a more liberal low-carb diet with higher carb intake (up to 100 grams/day) can help maintain your weight while reducing dietary restrictions. Monitor your progress and adjust as needed.
17. Is keto only for weight loss?
No, keto offers other benefits too! It can improve mental clarity, stabilize blood sugar, and potentially manage conditions like Type 2 diabetes and epilepsy. Individuals have also reported better appetite control and steady energy levels.
Wrapping Up: Is Keto Right for You?
The ketogenic lifestyle isn’t one-size-fits-all. While sticking to 20-50 grams of carbs per day on keto works for most people, fine-tuning your intake based on your needs will set you up for long-term success.
Start slow, track your meals, and listen to your body. Soon, ketosis will become second nature. With carb control mastered, you’ll experience all the benefits of the keto diet, from weight loss to enhanced mental performance.
Your Next Step:
Give keto a try by planning tomorrow’s carb, high-fat foods! If you’re sure whether keto is right for you, consult a healthcare provider or a registered dietitian to ensure it aligns with your health goals and medical conditions.
Sources
- American Journal of Clinical Nutrition: Ketogenic Diet Study
- National Institutes of Health: Keto and Weight Loss
- Nutrition & Diabetes: Keto for Blood Sugar Control
CTA: Schedule a consultation with our certified nutritionists today for personalized keto coaching!


